Skin irritations
Dermatitis is a term used to describe inflammation of the skin, regardless of its origin. In fact, the causes are numerous and often involve multiple factors.
There are two types of dermatitis:
- Irritant contact dermatitis
- Allergic contact dermatitis
The visible consequences are usually inflammation with erythema, tightness, itching and peeling.

To support your patients
Co-prescription
Irritant contact dermatitis
Irritant dermatitis is linked to a non-immunological inflammatory reaction caused by one-time or repeated skin contact with an irritating agent.
It occurs within hours of contact with the agent and disappears if contact with the irritant is not repeated.
Lesions vary in appearance, from simple redness to the formation of blisters, accompanied by tingling or burning sensations.
The lesion extends little or not at all beyond the area of contact with the irritant.
Irritant dermatitis has a variety of causes:
- Mechanical
- Chemical
- Climatic
- Infectious (bacterial or fungal in origin)
Mechanical irritant contact dermatitis
Dermatitis due to occlusion or repeated, prolonged rubbing with an irritant.
Diaper rash
Irritant erythematous dermatitis of the buttocks and thighs due to prolonged contact with particularly irritating urine and feces, or simply as a result of friction and/or occlusion with synthetic diaper fibers, leading to maceration and the deterioration of the barrier function.
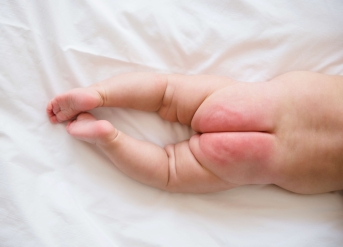
Climatic irritant contact dermatitis
Dermatitis due to an aggressive climatic environment and/or temperature variations.
Chapping and cracking
Caused by dehydration, these small cracks affect the hands, face, lips and parts of the body most exposed to the weather.
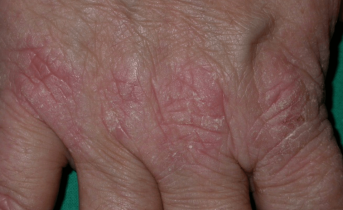
Chemical irritant contact dermatitis
Dermatitis caused by the one-time or repeated application of a chemical substance to the same area of skin, such as detergents, cleaning products, metals (nickel, etc.), organic solvents and certain surfactants in cosmetics.
Irritant hand dermatitis
Very common in the workplace.
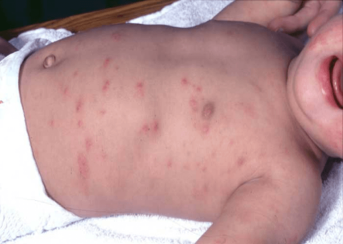
Infectious irritant contact dermatitis
They come from:
Bacterial, caused by streptococcus and/or staphylococcus.
Impetigo
Folliculitis
Fungal
Intertrigo
Parasitic caused by Sarcoptes scabiei hominis
Scabies in babies
Multifactorial irritant contact dermatitis
Dermatitis caused by exposure to numerous factors that act in synergy.
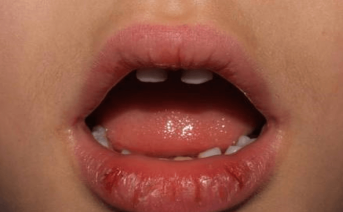
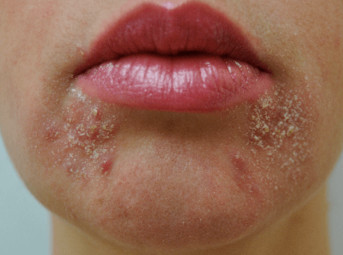
- Perioral dermatitis
- Angular cheilitis, prurigo, vulvitis
- Palmar dyshidrosis
Allergic contact dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis is linked to an allergic inflammatory reaction due to cellular immunological hypersensitivity to an exogenous substance (which becomes an allergen).
Following direct application or airborne transmission of an exogenous agent:
- This agent acts as a hapten, which transforms into an allergen in the epidermis after coupling with a protein
- Triggering a hypersensitivity reaction with a delayed cellular response
This type of dermatitis is more common in adults, and occurs after a latency period of a few days to a few years between the time of first exposure to the allergenic product and the time of re-exposure which induces eczema.
Patch tests or prick tests detect allergens.
In the news

Summaries of publications and clinical results
Find all our summaries by expertise.
View all summariesWant to read on?
This access is reserved for professionals, registered on Pierre Fabre For Med.
To access the full content, please register or log in if you already have an account.

