Publication Summary
Effective inhibition of Th17/Th22 pathway in 2D and 3D human models of psoriasis by celastrol enriched plant cell culture extract
Objective
Evaluate the immunomodulatory effect of Celastrol in in vitro models of psoriatic inflammation.
Celastrol is a triterpene produced in vitro from Tripterygium Wilfordii plant cell culture (patented technique developed by the Pierre Fabre Research Center's biotechnology unit).
Methodology
Preincubation of human CD4+ T lymphocytes (hCD4), normal human keratinocytes (NHEK), micro-epidermis and reconstructed human epidermis (RHE) with Celastrol and reference controls
Evaluation Criteria
Quantification of psoriasis biomarkers by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
Results
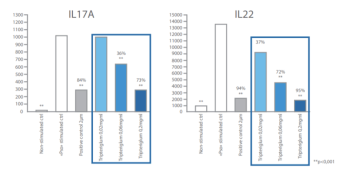
* CD4+ T LYMPHOCYTES
Celastrol inhibits IL-17A and IL-22 cytokine production in a dose-dependent manner
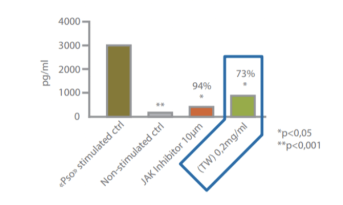
RECONSTRUCTED HUMAN EPIDERMIS:
Celastrol inhibits the production of the pro-inflammatory mediator IL-8
Conclusion
Celastrol modulates TH17/TH22 inflammation by acting on 2 targets: T lymphocytes and keratinocytes.
Our other publications on this subject
Want to read on?
This access is reserved for professionals, registered on Pierre Fabre For Med.
To access the full content, please register or log in if you already have an account.
