Summary of clinical results

Effects of Helichrysum Gymnocephalum in Pruritus associated to Atopic dermatitis
Pharmacological efficacy of Helichrysum Gymnocephalum in pruritogenic pathway in atopic dermatitis
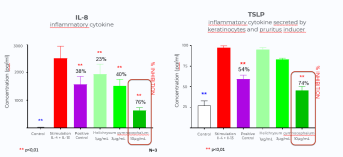
Anti-inflammatory effect of Helichrysum gymnocephalum on IL-8 and TSLP
Culture of keratinocytes (N= 3)
Creation of an inflammation simulation with keratinocytes stimulated by IL-4 and IL-13 for 24h
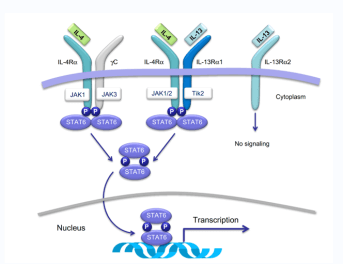
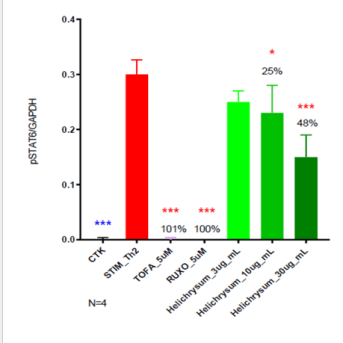
Anti-inflammatory effect of Helichrysum gymnocephalum on JAK 1/2-STAT6 pathway
JAK inhibitors are considered as the main treatments in Atopic Dermatitis.
It was, therefore, important for us to carry out a pharmacological study in the JAK pathway to compare the efficacy of our active ingredient to JAK inhibitors.
IL-4/IL-3 Stimulation : 15min
STAT6 phosphorylation
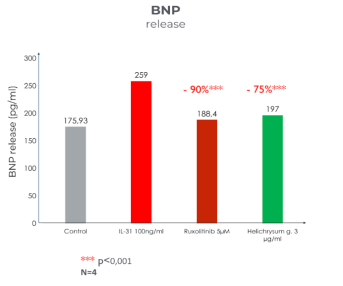
Important communication link between IL-31 and Brain Natriuretic Peptide (BNP)
IL-31 plays a major role in pruritus by causing the multiplication and development of neuritis (neurosensory fibers) via biomarkers such as BNP. Augmented release and synthesis by IL-31 of BNP might contribute to central and peripheral itch signaling.
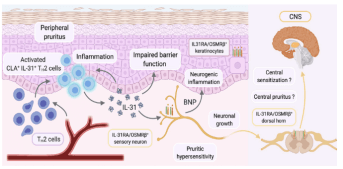
Anti-inflammatory effect of Helichrysum gymnocephalum on Brain Natriuretic Peptide (BNP)
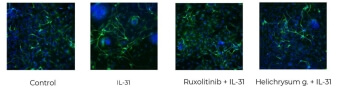
Co-culture of sensory neurons and keratinocytes.
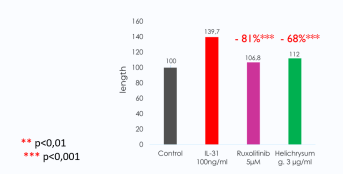
Anti-inflammatory effect of Helichrysum gymnocephalum on nerve growth
Co-culture of sensory neurons and keratinocytes.
.
Conclusion
Helichrysum gymnocephalum extract inhibits :
- The production of TSLP and IL-8
- The phosphorylation of JAK/STAT pathway
Helichrysum gymnocephalum has demonstrated its effectiveness in blocking neurite outgrowth as well as the production of BNP.
There is, thus, a specific anti-inflammatory and antipruritogenic properties for Atopic Dermatitis through JAK/STAT pathway.
More summaries of clinical results
Want to read on?
This access is reserved for professionals, registered on Pierre Fabre For Med.
To access the full content, please register or log in if you already have an account.